지역개발로 인한 농촌마을 경관변화요인 평가 및 분석연구 : 전라도 지역을 대상으로
This is an Open-Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0), which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
In this study, it was promoted for the purpose of direction for rural landscape planning and management through the analysis of the factors of change in the rural landscape. In the course of research, through literature review study and field surveys, to derive the 25 factors that influence the change in the rural landscape. Later, 25 factors were evaluated in the impact on landscape by experts. 25 factors of the rural landscape were a comprehensive analysis and the results of literature review study and field surveys about the five villages of research area; Ji-San village, Non-Gae village, etc. Expert evaluation was carried out by the rural landscape, and architecture professionals of various related fields. As a result of the analysis, the flow of rural development policy and the business had a great effect on the physical changes in the rural landscape. Furthermore, additional factors such as population structure and lifestyle have made the change in the complex landscapes. Meaning the study has is to provide information on what need there are considered factors in the rural landscape planning and management. The reason is that, since the rural landscape characteristics are different, in order to develop the more efficient rural landscape plan and management.
Keywords:
regional development, rural landscape planning, landscape changesI. 서론
공공재적 성격을 띄는 경관자원은 양적성장, 정주여건 개선과 도시형 개발 등에 초점이 맞추어진 농촌 지역개발 초기에는 관심이 미약했지만, 2000년대 이후 환경파괴, 웰빙 등의 사회적 흐름과 함께 농촌 지역개발에도 마을 만들기, 마을 가꾸기의 개념이 함께 논의되고 2007년 경관법 제정 이후 농촌경관도 농촌마을 종합개발사업의 일부로 자리매김하게 되었다.
농촌마을 종합개발사업의 일부분으로 실행되고 있는 권역단위 경관계획은 장기적 관점에서의 도, 시ㆍ군별 경관기본계획과는 달리 현실적인 측면에서의 실행적 내용을 담고 있으며, 농촌지역의 부존자원에 대한 새로운 시각에서의 다양한 가치들을 부여하며 가치의 재해석과 평가가 이루어지고 있다(Kim & Yang 2009). 그간 전통마을을 개선하면서 지붕개량, 취락구조개선, 농촌생활환경 개선 사업등이 추진되었는데 이 과정에서 새로운 집단계획마을을 형성하게 하였고 마을의 기능적 개선에 대한것은 부인할 수 없으나 아름다운 고유의 풍경을 살리지 못했다는 것은 아쉬움으로 남아있다(Chong & Ku 2007). 이러한 분위기에서 2013년 경관법의 전면 개정이 공포되고, 2014년 시행 되면서 인구 10만 초과 시ㆍ군의 경관계획 의무화 및 경관 심의제 시행이 제도화 되었지만 국토경관 관리 체계 중심의 내용으로 농촌의 경관을 체계적으로 보전ㆍ형성ㆍ관리하기에는 실천적 실효성이 낮은 상황이다.
이러한 문제인식으로부터 본 연구에서는 새마을운동부터 본격적으로 지역개발이 이루어진 1960년대 이후 현재까지 지역개발의 주요한 흐름과 이들이 농촌 경관에 어떠한 요인의 형태로 영향을 미쳤는지 그 특성을 파악하고, 이러한 변화요인들이 어떠한 측면에서 영향을 미치는지의 정도를 전문가 평가를 통해 고찰함으로써 향후 바람직한 농촌경관계획과 관리 방향에 시사점을 제안해보고자 한다.
Ⅱ. 이론적 배경
1. 농촌지역 개발을 위한 정책 및 사업 현황
농촌지역개발사업은 1962년 농촌진흥법의 공포에 따른 농촌진흥청 확대ㆍ개편과 함께 본격적으로 진행되기 시작하였다. 현재 우리나라의 지역발전정책은 여러 법률에 따라 다수의 주체가 독립적으로 추진하며, 중앙부처차원에서는 국토교통부, 행정자치부, 농림축산식품부 등이 핵심적인 역할을 담당한다(Kang et al. 2011).
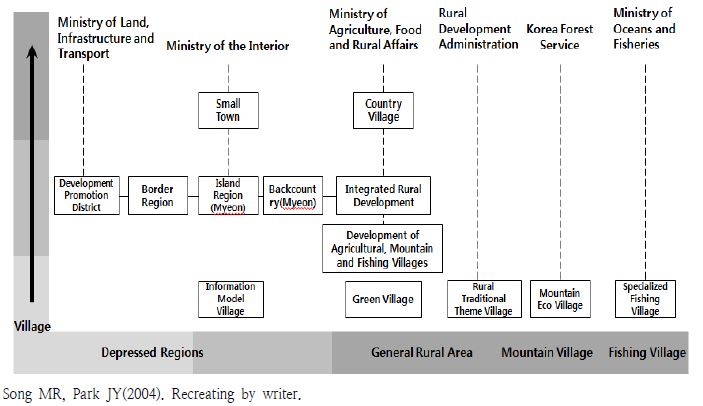
공간범위 기준으로는 각 중앙부처별로 정보화마을(행자부), 녹색농촌체험마을(농식품부), 농촌테마마을(농진청), 산촌생태마을(산림청) 등 다양한 마을단위 사업과 함께 농산어촌 개발사업과 같이 마을보다 규모가 더 큰 권역단위 개발사업, 낙후된 읍을 대상으로 하는 소도읍 육성사업 등 다양한 공간 범위를 대상으로 사업이 추진되었다(Fig. 1).
2. 농촌지역개발 정책 및 사업에서 나타난 경관개선의 특징
과거부터 현재까지 농촌지역에 추진되어 온 정책과 사업을 시기별로 살펴보면 사회적 분위기와 연관된 일련의 흐름을 살펴 볼 수 있다. 시행초기(1970년대)는 양적 성장을 목표로 추진되었던 시기로, 식량자급증산 관련 정책과 1차 국토종합개발계획을 중심으로 새마을운동, 취락구조 개선사업 등 기반시설 확충과 환경개선 등의 단일 목적으로 추진되었다. 80년대 들어서면서 2차 국토종합개발계획과 함께 농어촌 주거환경 개선사업, 농가 주거환경 개선사업 등 농업생산 위주에서 농촌 공간의 관점으로 접근한 개발방식이 도입되었으며, 90년대부터는 문화마을 조성사업, 오지 종합개발사업 등 본격적으로 낙후지역의 개선과 농촌관광 등을 고려한 종합적인 성격의 개발이 이루어지게 되었다. 2000년대 이후에는 어메니티 중심의 계획과 개발이 이루어지면서 농촌 경관은 생산성 향상을 포함한 환경개선, 주거편의 개선, 정주환경 개선, 농촌다움 발굴과 정체성 확보를 위한 중요한 역할로 대두되었음을 알 수 있다(Table 1).
즉, 농촌 지역개발에 있어 ‘농촌경관’이 직접적으로 고려되기 시작한 것은 2000년대 이후 부터이지만 새마을운동 이후 농촌 지역개발이 이루어지면서 토지이용형태, 산업구조, 인구구조 등이 크게 변하였고 이로 인해 경관은 지속적으로 변화를 겪어왔다.
III. 연구방법
1. 지역개발에 대한 농촌마을 경관변화 특징 및 요인의 도출
본 연구에서는 체계적인 논지의 전개를 위하여 선행연구 등 이론적 검토와 현장조사, 전문가 조사의 순서로 진행하였다. 이론 검토에서는 농촌경관 및 농촌지역개발에 대한 각종 연구논문, 정기간행물 등의 선행연구결과 항목들을 조사하였다. 이를 토대로 마을 현장에서의 변화와 정책ㆍ사업의 영향을 면밀히 비교하기 위하여 마을 대표와 면사무소 담당자에 대한 인터뷰 조사, 현장조사를 수행하여 농촌경관의 변화양상의 특징을 분석하였으며 최종적으로 전문가 평가를 통해 변화요인들과 경관과의 상관관계를 검토하고자 하였다.
현장조사 대상지 선정 과정에서는, 토지이용, 인구변화, 정책 및 사업 등 농촌경관 변천에 많은 영향을 주는 요인들에 대하여 농업이 주요 소득원인 전라도 지역을 대상으로 10년 단위의 토지이용 변화, 인구변화, 정책변화 등을 분석하여 대상지를 선정하였으며 군단위에서 인구, 토지이용의 변화가 가장 큰 지역과 작은 지역을 분류하여 5곳의 대상지를 도출하였다(Table 2).
조사 대상지는 경관 및 소득 사업의 진행으로 사업 유형에 따른 경관 변화를 확인할 수 있는 마을(원연장마을, 논개마을), 토지이용, 인구이동 등의 변화가 적고, 사업이 진행되지 않아 경관 변화 요인이 적은 마을(가목마을), 토지이용, 인구이동 등의 변화가 크고, 사업이 없어 경관이 자연적으로 변화되고 있는 마을(지산마을) 등 농촌경관의 보전ㆍ관리형태에 따라 구분하였는데, 최근 농림축산식품부에서 추진하는 국가농업유산 지정지역을 추가검토하여 생활, 자연, 생산경관에서 과거의 전통 농촌마을의 모습을 유지하고 있는 농촌경관의 유형을 포함하여 조사함으로써 지역개발과 농촌경관의 관계성을 검토하고자 하였다. 현장조사는 크게 두가지 부분으로 나뉘는데 우선, 마을대표와 면사무소 담당자 인터뷰 조사를 통해 경관요소 및 변화 양상, 관련 사업 추진현황, 시대별 경관변천 현황, 마을경관의 특징적 요소 등을 파악하였으며 그 후에 마을 현장조사로 사진자료를 확보하였다.
이론검토, 현장조사와 인터뷰조사를 통해 얻은 결과를 종합하여 전문가들의 평가를 위해 농촌마을의 경관변화요인 항목을 인구구조, 공간구조, 삶의질, 농산업구조, 농촌경관정책, 개발 및 토지이용 등의 분류 항목에 대하여 25개 항목으로 구성하였다(Table 3).
2. 농촌마을 경관변화요인 전문가 평가
본 연구의 관련 전문가는 다양한 관점에서의 객관적인 평가를 위해 농촌경관, 지역개발, 생태계획, 건축 등 다양한 분야에서 학술적, 실무적으로 경험이 있는 전문가를 대상으로 선정하였다(Table 4).
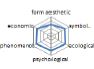
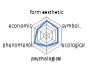
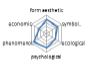
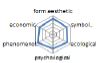
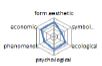
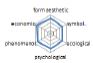
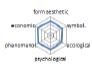
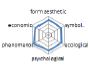
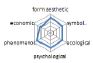
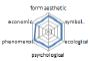
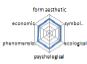
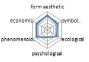
농촌경관 변화요인들의 외적, 내적 속성에 대한 경관분석을 위하여 ① 경관의 외형적 인자를 판단하는 형식미학적 측면, ② 경관의 상징적 의미에 대한 상징미학적 측면, ③ 토지이용, 생태적인자, 인간의 활용에 대한 생태학적 측면, ④ 인지도, 선호도에 대한 심리학적 측면, ⑤ 인과관계에 의한 관계를 살피기 위한 현상학적 접근, ⑥ 금전적 가치에 대한 경제학적 측면 등 6가지 기준을 토대로 평가가 이루어졌다. 이들 요인 항목들은 설문조사에 일반적으로 사용되는 5점 리커트 척도(전혀 그렇지 않다: 1, 매우 그렇다: 5)를 사용하여 측정하였다(Table 5).
Ⅳ. 결과 및 고찰
1. 지역개발에 대한 농촌마을 경관 변화의 특징
농촌지역개발 정책 및 사업을 통해 나타난 경관 변화 특징의 시사점에 근거하여 실제 농촌마을의 생산경관, 생활경관, 자연경관 등 경관 변화를 살펴보기 위해 인터뷰 조사를 통해 마을경관의 특징적 요소를 관찰 할 수 있는 지점을 기준으로 변화 양상을 분석하였다. 분석 결과, 각 마을이 보유하고 있는 경관 요소가 상이하게 나타났는데 특히 농촌마을의 자연경관은 비교적 과거시점과 동일하게 유지되고 있으나 생활경관은 사업ㆍ정책의 영향을 크게 받았으며 생산경관은 시기별 주요 작물 및 축산업 유무에 따라 다르게 나타나는 특징을 보였다(Table 6).
원연장마을과 논개마을은 농촌진흥청에서 추진하는 전통테마마을, 도에서 추진하는 향토마을 만들기사업 등 경관 및 소득 사업의 진행으로 관광마을화 되면서 생활경관을 중심으로 경관에 변화가 있는 것으로 나타났다. 사업이 진행되지 않은 가목마을과 지산마을은 농업시설물과 주민 이주 등 생활양식과 사회적 변화에 의한 경관변화가 관찰되었으며 전통경관을 보존하기 위해 노력하는 삼지내 마을은 대부분의 마을에서 나타났던 주거지 개량으로 인한 경관변화가 미미한 것으로 조사되었다(Table 7).
1960년대에는 벼농사가 생산경관의 대부분을 차지하였으나 농촌근대화촉진법과 개발사업이 시작되면서 비닐하우스, 창고 등 농업 시설물의 등장은 경관에 큰 변화 요인으로 작용하여 80년대부터 특용작물 재배, 축산업 등으로 지속적인 변화를 겪은 것으로 관찰되었다. 2000년대 이후에는 농촌관광을 기반으로 하는 다양한 사업이 추진되면서 2, 3차 산업을 위한 가공식품 작업장 등 새로운 생산시설이 나타났다. 또한, 어메니티에 대한 인식이 강화되면서 다랑논과 같은 독특한 경관을 보전하려는 움직임이 있었는데, 결국 60년대 새마을운동, 경지정리 등 농촌의 근대화 정책과 함께 비닐하우스와 같은 농업시설물의 등장으로 이전의 불규칙한 농지의 벼농사 위주 생산경관에서 규칙적인 농지와 다양한 시설물, 마을경관과의 연계 등의 생산경관으로 변화하게 된 것으로 보인다.
초가집 중심의 주거지 경관에서 1980년대 이후 마을 면적 확장 및 주거지 개량으로 경관에 변화가 나타나기 시작하여 2000~2010년대 이후 마을 경관사업 및 주민활동으로 공공건축물 건축, 마을 내 도로 포장 등 변화가 관찰되는 양상으로 나타났다. 특히 2000년대에는 농촌마을 가꾸기 사업의 일환으로 지붕과 가옥 외벽 등 리모델링 사업과 마을 내 수로, 담장이 생활경관에 영향을 미치고 있는 것으로 조사되었다. 2010년대 이후에는 공공건축물이 건축되기 시작하면서 커뮤니티 공간의 형태로 특징적인 모습이 보였다.
2010년대 이후에 생태와 환경을 보전하는 방향의 정책이 나오기 전까지 자연경관은 지역개발이 이루어짐에 따라 경지면적을 넓히는 경지정리로 농지가 확대되면서 일부 산지경관이 논과 밭으로 변하여 면적이 줄거나 형태가 바뀌는 형식으로 경관의 변화가 관찰되었다.
우리나라의 지역개발 방향의 흐름에 대하여 실제 농촌마을들의 경관변화 특징을 살펴보면 지역개발 초기단계에는 환경 개선에 중점을 두면서 경지정리와 비닐하우스 등 농업시설물의 등장과 지붕개량사업으로 초가집이 사라지고 새마을 운동으로 마을회관이 조성되어 마을공간 곳곳에 전반적인 변화가 일어났다. 80~90년대에는 주거환경 편의성 증진을 위한 주택개량과 마을길 포장사업, 농로정비 등 공간 계획적인 요인들이 두드려졌으며 2000년대 이후에는 관광기반 관점으로 현대식 개발과 보존위주의 생활경관의 모습이 복합적으로 나타났다. 어메니티와 삶의질 향상에 대한 관심이 증대하면서 마을가꾸기에 대한 필요성이 대두되었고 이러한 사회적 분위기와 흐름에 따라 경관의 보전, 복원의 움직임이 일어나게 되었다(Table 8).
2. 농촌마을 경관변화요인 전문가 평가 결과
농촌지역의 인구구조와 관련이 있는 고령화, 귀농귀촌, 다문화 가정 등의 요인들은 현상학적 측면에서 경관에 미치는 영향이 큰 것으로 분석되었다. 농촌에 실제로 거주하며 살아가는 주민의 인구학적 특성은 영농활동, 생활활동, 토지 이용 등 주민의 생활 행태와 밀접한 연관이 있기 때문으로 사료된다. 또한 마을의 과소화나 정주공간의 변화, 지리적 마을입지와 같은 공간구조 요인과 농촌경관정책은 시각적으로 보이는 경관의 외형적 모습에 직접적으로 미치는 영향이 큰 것으로 나타났다.
특히 25개의 경관변화 요인중에서 최근 몇 년 전부터 농촌정책의 중심 키워드로 나타나고 있는 6차산업, 농촌관광, 지역개발사업, 경관관련 법제도, 주민참여형 경관관리 등은 6개의 평가기준 항목에서 전반적으로 높게 나타난 점이 특징적인데 이들 요인은 여러 가지 측면에서 농촌경관에 중요한 영향을 미치는 요인이라는 의미로 해석할 수 있다.
6차 산업은 주민의 소득구조와 연관이 있을 뿐만 아니라 6차 산업을 위한 기반조성, 방문객 등을 농촌으로의 인구유입을 유도하는 특성으로 인해 영향력이 크다고 분석된 것으로 보인다. 농촌관광 또한 같은 맥락에서 하드웨어와 소프트웨어적 측면 모두 고려 해야 하는 특징이 있으며, 마을의 과소화나 정주공간 변화는 주민의 삶의 터전에 대한 변화이기 때문인 것으로 사료된다. 지역개발사업과 법제도는 밀접한 관계가 있는 항목들로 농촌지역의 사회ㆍ문화적 특성과 자연생태 등 농촌마을의 이미지와 정체성을 결정하는데 중요한 요인으로 작용하고 있다. 각 경관 요인들의 이러한 특성을 바탕으로 농촌경관의 보전과 관리를 위한 방향을 고려하고 시행한다면 체계적이고 효율적인 과정으로 접근할 수 있을 것이다(Table 9).
Ⅴ. 요약 및 결론
농촌마을의 경관은 궁극적으로는 주민이 스스로 관리하고 가꾸는 방향이 바람직 하지만 공공재적인 특성으로 인해 우리나라 농촌의 현실에서 아직까지는 공공의 다양한 역할이 수반되어야 하는 상황이다. 또한 시각적 측면에서는 생산, 생활, 자연 등의 특징으로 구분이 가능 하나, 토지 이용적 측면에서는 사유지, 국유지 등의 문제가 함께 부각되기 때문에 주민 개개인에게만 맡길 경우 경제ㆍ사회적 이해에 따라 쉽게 변형될 여지가 있으며 법ㆍ제도적 측면에서는 경관법, 삶의질법, 농어촌정비법, 문화재법, 건축법, 자연환경보전법 등 다양한 부처의 다양한 법령과도 얽혀있는 복잡한 양상으로 어느 한 측면만을 고려해서는 농촌경관의 체계적인 계획과 관리가 효과적인 결과로 이어지기 어렵다.
그리하여 본 연구에서는 문헌분석과 현장조사를 통해 실제 농촌의 경관변화에 영향을 주는 다양한 요인들을 도출하고, 요인들이 어떠한 측면에서 경관에 어느정도 영향을 미치는지 전문가의 관점으로 살펴보고 분석함으로써 농촌경관 계획과 관리 방향에 대한 시사점을 제공하고자 하였다.
분석 결과, 농촌 지역개발 정책 및 사업의 성격과 흐름이 농촌경관의 물리적 변화에 지배적인 영향을 미치면서 인구구조, 생활방식, 삶의 질 인식의 변화 등 부가적인 요인들이 더해져 하드웨어, 소프트웨어 측면에서 복합적인 경관 변화가 이루어지고 있는 것으로 나타났다.
최근 생태, 복원, 보전, 삶의질, 치유 등의 키워드가 부각 되면서 지역개발 또한 예전과 같은 단순한 형태의 개발에서 중심지-배후지, 거주민-관광객, 소득과 역량개발 등 복합적인 형태의 개발 형태로 변화하고 있다는 점은 바람직하다고 여겨진다. 하지만 다양한 농촌지역에서 비슷한 목적을 가지는 지역개발이 이루어 질 때, 결과 형태가 유사하게 나온다면 과거의 획일화된 개발 방식과 큰 차이가 없을 것이다. 따라서 본 연구가 가지는 의미는 농촌경관 계획과 관리에 있어서 각 변화 요인들이 경관에 어떠한 측면에서 영향을 미치는지 정보를 제공하여 마을 현황에서 어떠한 요인을 우선적으로 고려해야 하는지 방향성을 제시하는데 있다고 하겠다.
고령화, 귀농귀촌, 다문화 가정 등 주민의 인구학적 특성은 시간이 흐름에 따라 지속적으로 경관에 큰 영향을 미치는 요인이기 때문에, 주민의 연령대나 가구의 특성, 유입인구 등에 대한 면밀한 분석을 통해 마을 주민들이 행할 활동과 생활 패턴을 미리 예측하는 것도 경관관리를 위한 방안이 될 수 있을 것이다. 가령, 고령인 마을 주민과 귀촌한 주민을 비교하면 생활 동선과 활동 범위가 달라 생활경관에 큰 영향을 미치기 때문이다.
전문가 평가에서 농촌정책과 연관이 있는 6차 산업, 농촌관광, 지역개발사업, 경관관련 법제도 등은 6개의 평가기준 항목 전부에서 농촌경관에 중요한 영향을 주는 요인이라는 결과로 해석이 된 바, 그중 6차 산업, 농촌관광, 지역개발사업은 모두 주민의 소득원과 관련이 있다는 공통점이 있다. 즉, 소득과 연계된 부분에 대해서는 주민이 실질적으로 경관보다 소득에 더 비중을 두고 행동을 하기 때문에 주민에게 경관관리를 무조건 독려하기 보다 이러한 점을 고려하여 마을 공간별 관리의 차등화가 필요할 것이다. 더불어, 경관의 이미지와 정체성 제고를 위해서는 현대 농촌의 생활 양식을 세련된 형태로 구현할 수 있는 물리적 재료소재와 내구성의 향상과 같은 기술적 방안이 동시에 수반되어야 할 것으로 사료된다.
하지만 본 연구에서는 전라도 지역만을 대상으로 하여 전국단위의 다양한 대상지를 통한 일반화된 방안을 검증하지는 못하였으며, 평가의 기준을 세분화하지 못하여 실제 농촌과의 비교ㆍ적용을 통한 구체화된 대안을 제시하기에는 한계점이 있다. 따라서 주요 공간의 경관이미지 분석 등 경관구조 분석 방법의 다양화와 평가항목의 세분화, 조사 대상지의 확장을 통해 미래 농촌경관에 영향을 줄 수 있는 요인에 대한 구체적인 대안 마련을 위한 후속 연구가 필요할 것으로 여겨진다.
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science & Technology Development (Project No. PJ01164501)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
References
- Chong, GC, Ku, GH, (2007), A study on structure and planning of landscape in village, J Korean Inst Rural Archit , 9(1), p1-8.
- Ha, ME, (2013), A study on changing process of community and spatial structure by rural development project, Master’s thesis in Seoul National University.
- Hong, SK, Rim, YD, Nakagoshi, N, Chang, NK, (2000), Recent Spatio-temporal Changes of Landscape Structure, Heterogeneity and Diversity of Rural Landscape, J Ecol Environ , 23(5), p359-368.
- Kang, YE, Choi, DW, Hong, SH, Im, SB, (2009), A study on the changes of rural landscape in modern times. , 2009 Conference of Korea Landscape Council, p126-138.
-
Kang, YE, Choi, DW, Hong, SH, Jung, YH, Kim, SB, Im, SB, (2011), A study on rural landscape change by government’s development policy, J Korean Inst Landsc Archit, 39(6), p21-35.
[https://doi.org/10.9715/KILA.2011.39.6.021]

- Kim, SH, (2001), Landscape structure and change in chuncheon, Master’s thesis in Kangwon National University.
- Kim, SH, Yang, BE, (2009), A Study on Rural Landscape Planning Based on Rural Village Landscape, J Korean Inst Landsc Archit , 37(3), p82-90.
- Lee, HJ, (2009), Preference of the landscape change in the rezoned residential districts, Ph.D thesis in the University of Seoul.
- Lee, JC, (2010), A design of housing complex based on spatial structure of traditional villages, Master’s thesis in Gwangju University.
- Lee, SY, Jang, M, Shim, JY, Heo, J, (2010), A study on the change of landsc in Korean rural village, J Korean Inst Traditi Landscape Archit , 28(4), p112-119.
- Song, MR, Park, JY, (2004), Consolidation and Streamlining of Rural Development Programs and Projects, Korea Rural Economic Institute.
-
Ra, JH, Lee, YE, Cho, HJ, Ku, JN, Kwon, OS, (2013), Development and application of landscape diversity evaluation model on the basis of rural and natural area, J Korean Inst Landsc Archit , 41(6), p84-95.
[https://doi.org/10.9715/KILA.2013.41.6.084]

- Won, SH, (2010), A study on the spatio-temporal change of urban land use according to the change of accessibility, Master’s thesis in Kyunghee University.
- Yoon, WK, (2004), Directions and tasks of rural planning system in Korea, Korean J Agric Ext , 11(1), p111-123.